Purchase discounts lost is a general ledger account that contains the amounts a business did not save through its failure to take early payment discounts offered by suppliers. This information is aggregated for reporting to management, and is also used for subsequent analysis to improve the payment processing procedure. This account usually contains too small an amount to report it separately in the financial statements, so it is instead aggregated into another line item for reporting purposes. The account called Purchases is only used with the periodic inventory system.
Receiving Payment from Customers
Sales Discounts is a contra revenue account that records the value of price reductions granted to buyers in order to incentivize early payments. Examples include Net D cash discounts like 2/30 Net 60, where a full invoice payment is due in 60 days but a buyer will receive a 2% discount in case of an early settlement within 30 days. In the accounting entries, when the purchase is made, the purchases account is debited for \$1,800, and accounts payable is credited for the same amount. Upon payment, accounts payable is debited for \$1,800, cash is credited for \$1,746, and the purchase discounts account is credited for \$54. This reflects the reduction in the liability and the impact of the discount on the inventory value. Discounts allowed and discounts received are vital in business transactions.
Accounting for Purchase Discounts: Net Method vs Gross Method
Local Tech, the retailer, purchases smartphones from a supplier, Mobile Distributors, for $5,000 under the same payment terms (2/10, net 30). Local Tech pays within 10 days to take advantage of the discount. The 2% discount equates to a payment reduction of $100, so the final payment made by Local Tech is $4,900.

Purchase discount journal entry
With every day that the payment is not received, theseller or receivable has an opportunity cost– in terms of the financial returnhe could have otherwise generated. Cash increases (debit) and is purchase discount a debit or credit Sales increases (credit) by $37,500 (250 × $150), the sales price of the phones. Since the computers were purchased on credit by the customer, Accounts Receivable increases (debit) and Sales increases (credit) by the selling price of the computers, $15,000 ($750 × 20). Let’s continue to follow California Business Solutions (CBS) and the sale of electronic hardware packages to business customers. As previously stated, each package contains a desktop computer, tablet computer, landline telephone, and 4-in-1 printer.
- The debit and credit sides of the trial balance should be equal.
- Companies using periodic inventory don’t update the Merchandise Inventory account when purchases or sales are made.
- Since the customer already paid in full for their purchase, a cash refund of the allowance is issued in the amount of $200 (20 × $10).
- If the buyer does not take the discount, then accountants do not make the second entry.
- When a company purchases goods on credit, it discusses the repayment terms with the supplier.
Difference Between Discount Allowed and Discount Received
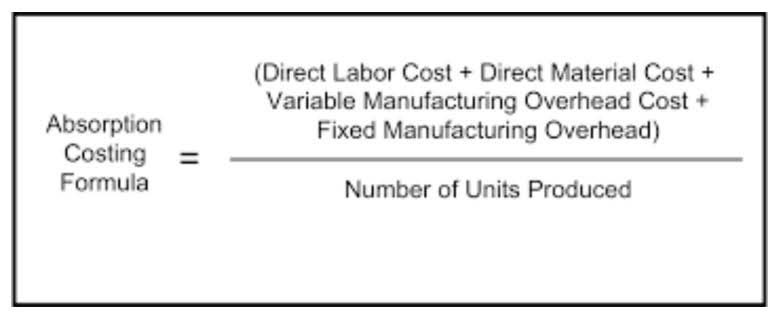
Initially, when inventory is purchased, Inventory and Accounts Payable increase. Upon payment within the discount period, Accounts Payable is debited for the full amount, Cash is credited for the discounted amount, and Inventory is credited for the discount. This ensures that the total assets and liabilities remain balanced. In this section, we illustrate the journal Liability Accounts entry for the purchase discounts for both net methods vs gross method under the periodic inventory system. In this journal entry, the purchase discounts is a temporary account which will be cleared to zero at the end of the period.
Purchases under a Periodic System

However, the company could benefit by paying less to its suppliers for the same products or services that it purchases. From an accounting perspective, it can be seen that when the purchase is made (and the invoice is generated), the journal entry to record this transaction is Debit – Purchases, and Credit – Accounts Payable. This is mainly an incentive to the purchasing party to settle the bill earlier than the prescribed date. At the date of purchase the business does not know whether they will settle the outstanding amount early and take the purchases discount or simply pay the full amount on the due date. In these circumstances the business needs to record the full amount of the purchase when invoiced and ignore any discount offered in the supplier terms.
- In a periodic inventory system, purchase discounts reduce the value of inventory.
- This process ensures that the accounting equation remains balanced, with total assets equaling total liabilities plus equity.
- In the last 10 years, she has worked with clients all over the country and now sees her diagnosis as an opportunity that opened doors to a fulfilling life.
- He is the sole author of all the materials on AccountingCoach.com.
- After these entries, the net effect on ABC Company’s financials shows that inventory increased by \$1,800 and then decreased by \$54, resulting in a final inventory value of \$1,746.
- Cash increases (debit) for the amount owed to CBS, less the discount.
This purchase discount of $60 will be offset with the purchase account and be cleared to zero at the end of the accounting period. If we use the example above, the gain to the business of paying 1, days earlier than petty cash expected was the purchase discount of 30. The customer has not yet paid for their purchase as of October 6.

- A purchase discount is a small percentage discount a company offers to a buyer to induce early payment of goods sold on account.
- These discounts help businesses save costs and improve cash flow.
- These credit terms are a little different than the earlier example.
- The buyer records an offsetting credit to the cash account to record the payment of $4,900, and a credit to the purchase discounts account of $100 to record the discount.
- If the offered terms were not economical, there is no need to track them.
To calculate inventory cost, they multiply the number of each kind of merchandise by its unit cost. Then, they combine the total costs of the various kinds of merchandise to provide the total ending inventory cost. When taking a physical inventory, company personnel must be careful to count all goods owned, regardless of where they are located, and include them in the inventory. The debit to the Sales Returns and Allowances account is for the full selling price of the purchase. The $6 credit reduces the balance of the Sales Discounts account and the balance is the cash refund.

Cash discounts are recorded as an expense in the profit and loss account. Hence, the total accounts payable become a total of $15,000 ($1,470 + $30) the same as the original invoice amount. It reduces the expenses or cash outflow of the company, but it could not be considered the revenues under the accounting principle. On July 17, the customer makes full payment on the amount due from the July 7 sale. On June 8, CBS discovers that 60 more phones from the June 1 purchase are slightly damaged.
However, purchases are crucial to the operations of these companies. Usually, companies acquire goods for credit and pay for them at a later date. The Sales Discounts, Returns, Allowances contra revenue sales accounts may be presented on the income statement as individual line items or–if immaterial or preferable–aggregated into a single contra-revenue line. This is because the initial accounting journal entry at the time of sale was a debit to Accounts Receivable asset account and credit to a Sales Revenue account. A purchase return occurs when a buyer returns merchandise to a seller.

Leave A Comment